
What is UVGI
Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation (UVGI) is a type of electromagnetic radiation that is used to kill microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, yeast, mold, and fungi. It is a non-chemical technology with no residual by-products. The use of short-wavelength ultraviolet (UV-C) light to kill or inactivate microorganisms has been a widely accepted disinfection method since the mid-20th century. UV lamps for air disinfection (UVGI) have gained significant popularity in air purification, particularly in HVAC applications. Following the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the use of UVGI for HVAC has gained increased attention and recognition for its highly effective disinfection capabilities.
Importance Of UVGI
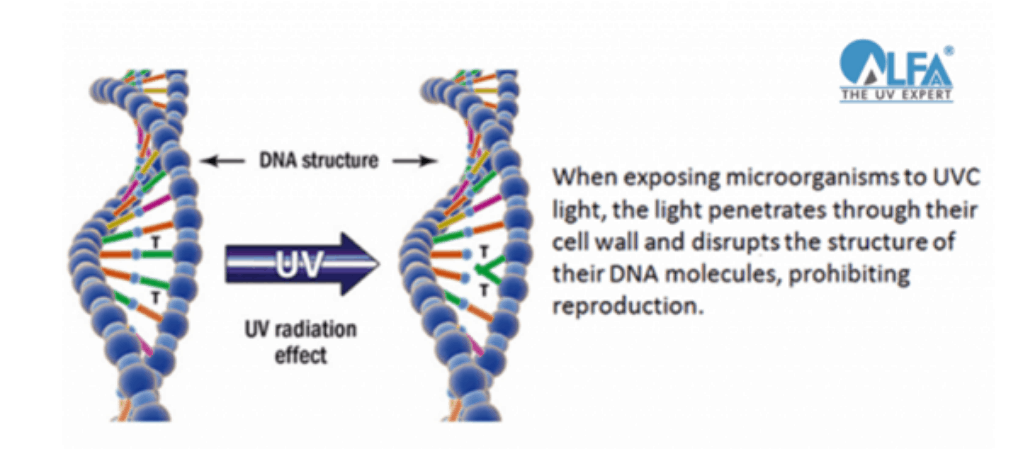
Ultraviolet light has demonstrated great potential in effectively disinfecting both air and surfaces. In response to the pandemic, governments and companies worldwide are adopting various sanitation practices, including the use of Ultraviolet (UV) light, a solution that has been in use for decades for effective disinfection. Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation (UVGI) has been successfully utilized in reducing airborne pathogens in healthcare environments. This technique utilizes light in the 250nm to 280nm wavelength range, known as the UVC range, to disrupt the DNA of harmful microorganisms, rendering them unable to reproduce, and consequently eliminating the spread of infection. ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers) recommends various strategies, including UVGI, to address disease transmission and promote healthy indoor environments.
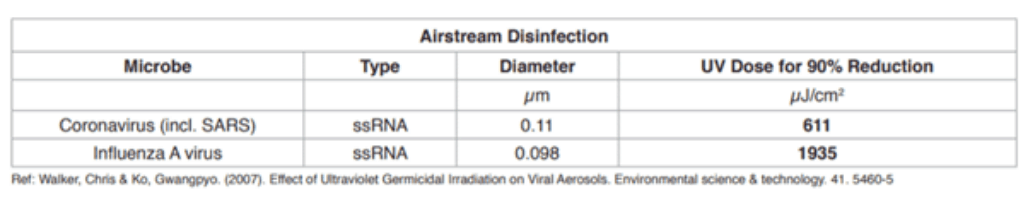
The coronavirus is highly susceptible to germicidal UV irradiation, with its susceptibility being greater than 3 times that of the influenza virus.
How In-Duct UV-C Lamp Arrays Affect Air Disinfection in HVAC
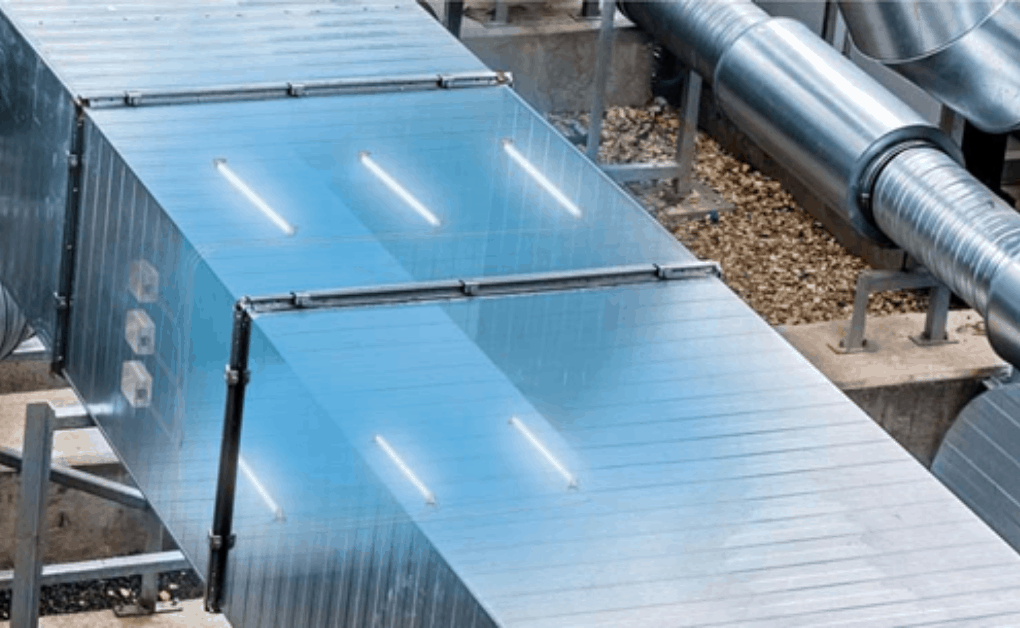

According to ASHRAE, in-duct ultraviolet germicidal irradiation (UVGI) systems can effectively disinfect pathogenic particles transported by air moving through ventilation systems. Proper design of these systems is crucial for both energy consumption and disinfection performance, as outlined in a recently published paper in Science and Technology for the Built Environment. Respiratory diseases pose a significant threat to public health and have adverse effects on society and the economy. Given that people spend most of their time indoors and in light of airborne infectious diseases like the current COVID-19 pandemic, measures to minimize the risk of airborne pathogen transmission are crucial for maintaining a healthy indoor environment.

