Development and production of drugs that are approved for use as medicines make up the pharmaceutical business. Regulations for the pharmaceutical industry are in place to guarantee the efficacy and safety of both generic and name-brand medications. It is crucial for pharmaceuticals to eliminate any risk of adverse effects on the users of the products in addition to adhering to industry norms and rules. This applies not only to pharmaceuticals but also to goods produced by the healthcare and cosmetics sectors.
Due to patients’ compromised immune systems and the risk of water to human contact, it is essential that the water used in these delicate areas be devoid of pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and others. Sterile working conditions are required in pharmaceutical manufacturing laboratories. A number of procedures rely on ultrapure water to create goods that are up to stringent quality requirements. Process fluids also utilize non-ultrapure water, which must be microbe-free to prevent bacterial colonization in the production facilities.

A method known as good manufacturing practice (cGMP) is used to guarantee that goods are consistently manufactured and monitored in accordance with quality standards. It is intended to reduce any production-related risks associated with pharmaceuticals that cannot be avoided through testing the finished product.
In the production, processing, and formulation of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), intermediates, and finished pharmaceutical products (FPP), as well as in the preparation of solvents and reagents and cleaning (such as washing and rinsing), water is frequently used as a raw material or starting material.
It is crucial to limit the hazards connected to the production, distribution, and storage of water while taking into accounts its characteristics and use.
- To ensure proper WPU, pre-treatment, Purification, storage, and distribution system design, installation, operation, and maintenance.
- To continuously or occasionally perform sanitization.
- To take the necessary precautions to prevent chemical and microbial contamination.
- To prevent microbial proliferation and endotoxin formation.
cGMP includes all areas of manufacturing, including raw materials, workspaces, and tools. Each process that can have an impact on the final product’s quality requires specific defined procedures. Systems must exist to show written evidence that the right steps are consistently taken at each stage of the manufacturing process, each time a product is manufactured. In the production of drug goods and drug compounds like Active Pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), pharmaceutical water and clean (pure) steam are employed as utilities and ingredients for Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) processes.
How Does the Pharmaceutical Industry Benefit from UVC Technology?
With a short wavelength of between 200 and 280 nm, ultraviolet-C (UVC) light has a germicidal effect and can destroy bacteria, viruses, and microorganisms. When exposed to UVC light, the thymine bases found in the genetic material DNA or RNA of the microbial contaminants react and produce a molecule. This restricts the growth of microorganism by killing them. As a result, UVC light disinfection systems are set up at various points during the production process in a variety of pharmaceutical sectors.
The pharmaceutical business uses UV technology to disinfect and deozonate water to the highest standards of purity. Pathogens that are resistant to chlorine can be eliminated by UV treatment. It successfully eliminates any contamination by interfering with germs’ DNA and stopping them from procreating further. For process sectors like the production of pharmaceuticals, this is essential. It has no negative effects on the product’s quality and delivers excellent outcomes by successfully treating common impurities. Manufacturers can guarantee efficient deozonation and disinfection to meet the requirements for pure water in each phase of the pharmaceutical business by using UV equipment.
The amount of energy or UV dose a microbe absorbs directly affects how well it can be disinfected. UV disinfection uses the first-order kinetic reaction. The amount of ultraviolet light that is applied directly relates to the microbiological kill rate. The kill rate will increase with increasing dose. It is advised to use a UV tube for no more than 6000 burning hours because the UV tube’s ultraviolet beam intensity reduces over time.
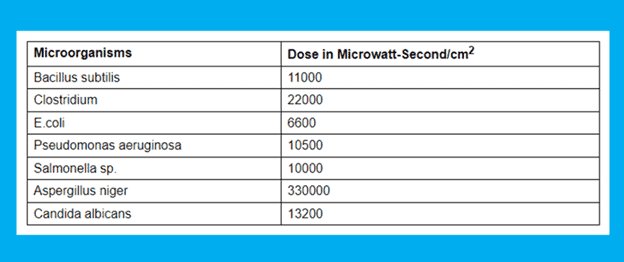
Image courtesy
Is UV Technology the best method for disinfection in the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals?
UV technology aids in the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals in the following ways,
Disinfection of microbial contaminants:
UV technology kills or inactivates the deadly bacteria present in production water and on the surfaces of machinery, pipes, and other physical assets in manufacturing facilities.
Ozone decomposition:
UVC light decomposes the ozone in the water. The microorganisms (mainly bacteria) that are present in the recirculation of water are inhibited or reduced by the ozonation.

